13 Nov 2024
Recent statistics indicate that approximately 40% of currently marketed drugs and nearly 90% of candidates in R&D pipeline belong to Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS) II or IV poorly water-soluble drugs. Consequently, enhancing drug solubility and improving bioavailability are pressing challenges in the realm of new drug development. Widely employed methods for solubility enhancement include:
API Salt Form Screening
API Micronization
Amorphous Solid Dispersion (ASD, Spray Drying & Hot-melt Extrusion)
Nanocrystals
Liquid-based Formulations
Permeability Enhancement
At Crystal Pharmatech, we specialize in overcoming the challenges associated with poorly water-soluble drugs. Our proven track record in crystallization and ASD formulation development, coupled with our commitment to scientific excellence, positions us as a reliable ally in achieving your scientific and regulatory goals.
API Salt Form Screening
Salt formation represents a straightforward and cost-effective method for solubilization. Organic weak acid or organic weak basic drugs can be converted into soluble salts, thereby increasing their solubility and improving oral bioavailability. Literature indicates that around 50% of drugs in the U.S. market exist in salt forms.
API Micronization
Micronization is a fluid dynamics-driven process that diminishes particle sizes to the micrometer range. In the context of APIs, micronization increases the specific surface area, porosity, and surface energy of the drug particles. This, in turn, enhances the solubility and bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs. Micronization has evolved into a well-established API technology, finding successful applications in both clinical and commercial products.
Amorphous Solid Dispersion (ASD, Spray Drying & Hot-melt Extrusion)
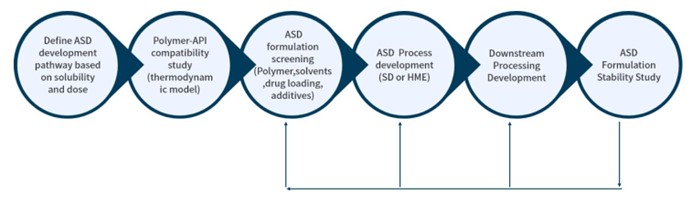
For poorly water-soluble drugs, amorphous solid dispersion (ASD) stands out as the preferred formulation for oral dosage forms. Both spray drying and hot melt extrusion methods can be utilized to prepare ASD, enhancing solubility and oral bioavailability.
Spray Drying
The spray drying process is a particle engineering technique that is a proven approach to improving the solubility of poorly soluble compounds. It has been widely used to enhance bioavailability in drug manufacturing for the following advantages:

Scalable and cost-effective technique
Consistent particle size control
Ability to handle temperature-sensitive molecule
Long-term stability
The core technical team at Crystal Pharmatech has solid knowledge and expertise in the fundamentals and scaling-up principles for spray drying process and commercialized several amorphous solid dispersion solid dosage form drug products. With our deep understanding of all quality and regulatory requirements and world-class manufacturing and analytical equipment, we are confident that we can support amorphous solid dispersion formulation development at high speed and with high quality.
Hot Melt Extrusion
HME is widely recognized as an effective technology that enhances the bioavailability of poorly soluble APIs, ultimately improving patient compliance and making the manufacturing process more efficient.

Can be operated as a continuous process, ensuring optimal reproducibility. Appropriate for large-scale production.
Less offline testing is required, and online PAT can be easily implemented.
A limited number of processing steps, short residence time, and reduction in labor forces lead to higher economic efficiency.
Solvent-free process, environmentally friendly.
Relatively high drug load possible.
Nanocrystals
Nanocrystal drugs are characterized by particle sizes in the nanometer range, typically below 1 μm (practically ranging from 200 to 500 nm). Formulations utilizing nanocrystals exhibit very small particle sizes, offering distinctive properties and benefits. These include heightened drug solubility, expanded surface area, improved bioavailability, and accelerated drug release.